v0.5.6 Cluster(Cassandra)
Note:
The current performance metrics are based on an earlier version. The latest version has significant improvements in both performance and functionality. We encourage you to refer to the most recent release featuring autonomous distributed storage and enhanced computational push down capabilities. Alternatively, you may wait for the community to update the data with these enhancements.
1 Test environment
Compressed machine information
| CPU | Memory | 网卡 | 磁盘 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 48 Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2650 v4 @ 2.20GHz | 128G | 10000Mbps | 750GB SSD,2.7T HDD |
- Starting Pressure Machine Information: Configure the same as the compressed machine.
- Testing tool: Apache JMeter 2.5.1.
Note: The machine used to initiate the load and the machine being tested are located in the same data center (or server room)
2 Test Description
2.1 Definition of terms (the unit of time is ms)
- Samples – The total number of threads completed in this scenario.
- Average – The average response time.
- Median – The median response time in statistical terms.
- 90% Line – The response time below which 90% of all threads fall.
- Min – The minimum response time.
- Max – The maximum response time.
- Error – The error rate.
- Throughput – The number of transactions processed per unit of time.
- KB/sec – The throughput measured in terms of data transmitted per second.
2.2 Low-Level Storage
A 15-node Cassandra cluster is used for backend storage. HugeGraph and the Cassandra cluster are located on separate servers. Server-related configuration files are modified only for host and port settings, while the rest remain default.
3 Summary of Performance Results
- The speed of a single vertex and edge insertion in HugeGraph is 9000 and 4500 per second, respectively.
- The speed of bulk vertex and edge insertion is 50,000 and 150,000 per second, respectively, which is much higher than the single insertion speed.
- The concurrency for querying vertices and edges by ID can reach more than 12,000, and the average request delay is less than 70ms.
4 Test Results and Analysis
4.1 Batch Insertion
4.1.1 Pressure Upper Limit Test
Test Method
Continuously increase the concurrency level to test the upper limit of the server’s ability to provide services.
Pressure Parameters
Duration: 5 minutes.
Maximum Insertion Speed of Vertices:
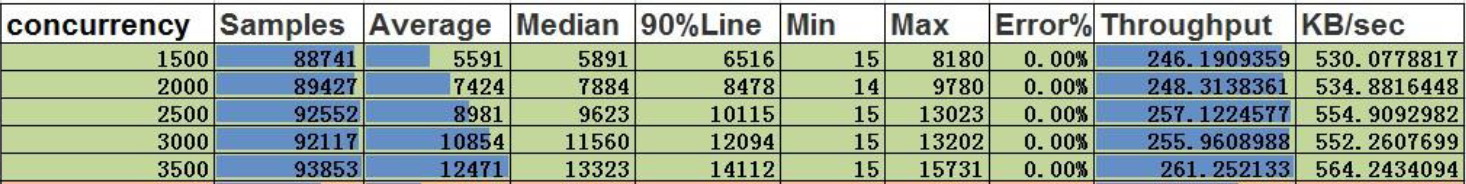
Conclusion:
- At a concurrency level of 3500, the throughput of vertices is 261, and the amount of data processed per second is 52,200 (261 * 200).
Maximum Insertion Speed of Edges:

Conclusion:
- At a concurrency level of 1000, the throughput of edges is 323, and the amount of data processed per second is 161,500 (323 * 500).
4.2 Single Insertion
4.2.1 Pressure Upper Limit Test
Test Method
Continuously increase the concurrency level to test the upper limit of the server’s ability to provide services.
Pressure Parameters
- Duration: 5 minutes.
- Service exception mark: Error rate greater than 0.00%.
Single Insertion of Vertices:
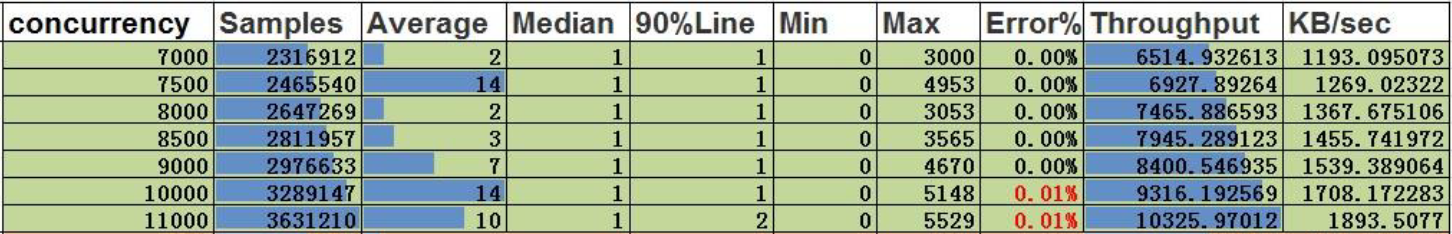
Conclusion:
- At a concurrency level of 9000, the throughput is 8400, and the single-insertion concurrency capability for vertices is 9000.
Single Insertion of Edges:
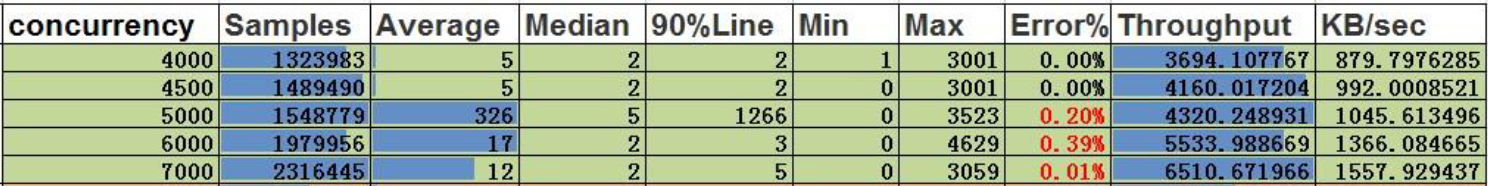
Conclusion:
- At a concurrency level of 4500, the throughput is 4160, and the single-insertion concurrency capability for edges is 4500.
4.3 Query by ID
4.3.1 Pressure Upper Limit Test
Test Method
Continuously increase the concurrency and test the upper limit of the pressure that the server can still provide services normally.
Pressure Parameters
- Duration: 5 minutes
- Service exception flag: error rate greater than 0.00%
Query by ID for vertices
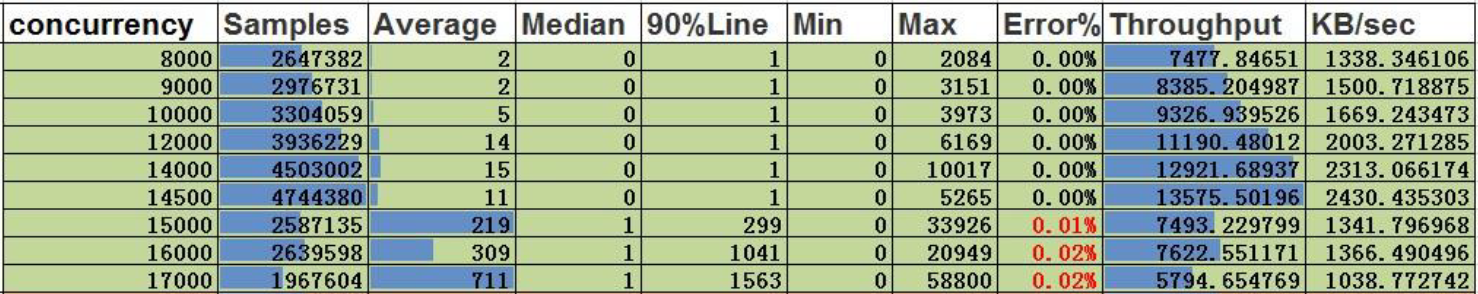
Conclusion:
- The concurrent capacity of the vertex search by ID is 14500, with a throughput of 13576 and an average delay of 11ms.
Edge search by ID
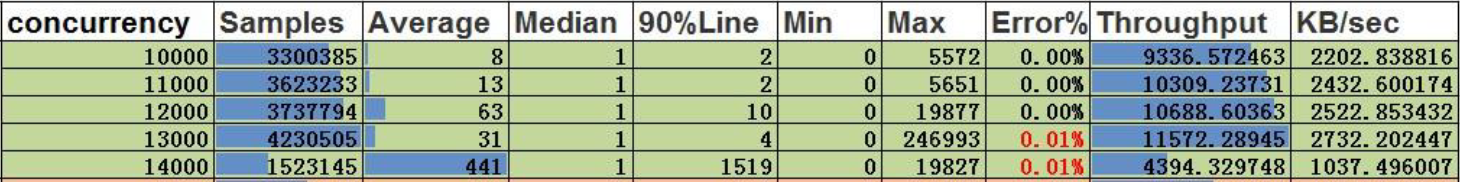
Conclusion:
- For edge ID-based queries, the server’s concurrent capacity is up to 12,000, with a throughput of 10,688 and an average latency of 63ms.